Business
Sponsored | What Are Cold Room Panels and How Do They Work?
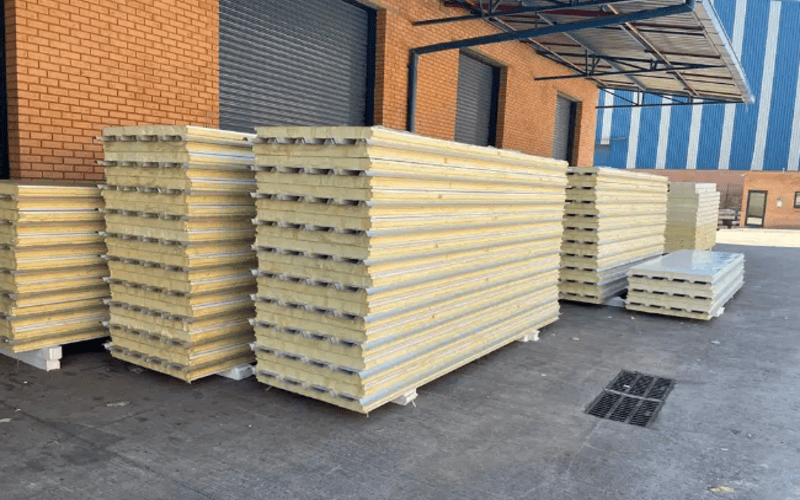

Cold room panels are essential components of cold storage facilities, designed to maintain controlled temperature environments for perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive items.
These panels form the insulated walls, ceilings, and floors of cold rooms and freezers, resulting in optimal thermal efficiency and energy conservation. They play a fundamental role in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and logistics, where temperature regulation is critical for product preservation.
Understanding Cold Room Panels
Cold room panels are prefabricated, insulated panels that provide the structural and thermal barrier needed for cold storage facilities.
These panels are typically made with an insulating core sandwiched between two outer layers of metal sheeting, usually stainless steel, galvanized steel, or aluminum.
The insulating core is commonly composed of polyurethane foam (PUF), polyisocyanurate (PIR), expanded polystyrene (EPS), or mineral wool, each offering varying degrees of thermal resistance, fire resistance, and moisture resistance.
These panels are manufactured with tongue-and-groove or cam-lock joint systems for an airtight fit that minimizes heat transfer and prevents the infiltration of moisture, which can compromise insulation performance.
How Cold Room Panels Work
The effectiveness of cold room panels lies in their ability to prevent heat exchange between the internal cold storage environment and the external surroundings. This is achieved through the following mechanisms:
- Thermal Insulation
The high-performance insulating core within the panels reduces heat conduction, maintaining the required temperature inside the cold room. Polyurethane and polyisocyanurate foams, for example, have low thermal conductivity, making them highly effective at preventing temperature fluctuations.
- Air-Tight Sealing
Cold room panels are designed to interlock tightly, preventing gaps that could allow warm air to enter or cold air to escape. This airtight seal minimizes condensation, which can lead to ice formation, mould growth, and reduced efficiency of the cooling system.
- Moisture and Vapor Barrier
To prevent water vapor from infiltrating the cold room, panels often have a protective layer that resists moisture. Excessive humidity can lead to frost buildup and compromise the integrity of stored products.
- Load-Bearing Capacity
In addition to their insulation properties, cold room panels also serve as structural elements. They can support ceilings and even withstand heavy loads in industrial cold storage applications.
- Fire Resistance and Hygiene Compliance
Many cold room panels are treated with fire-retardant materials to improve safety, especially in facilities where strict fire regulations are enforced. The smooth, non-porous surfaces of metal cladding also make them easy to clean, providing compliance with hygiene standards in food processing and pharmaceutical storage.
Applications of Cold Room Panels
Cold room panels are widely used in various industries, including:
- Preserving perishable goods such as meat, dairy, seafood, and frozen foods.
- Maintaining optimal storage conditions for vaccines, medicines, and biologics.
- Walk-in freezers and refrigerated display units.
- Restaurants and hotels use cold rooms for bulk food storage.
Cold room panels are essential in maintaining energy-efficient and temperature-controlled environments. Their durability and air-tight properties make them indispensable in industries where precise temperature management is vital.
Follow Joburg ETC on Facebook, Twitter , TikTok and Instagram
For more News in Johannesburg, visit joburgetc.com